15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 350 |
Published by VMT at Sep 12 2023
350 |
Published by VMT at Sep 12 2023
What is Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a versatile and environmentally friendly method of applying a protective finish to various products. Unlike traditional liquid paint, which is solvent-based, powder coating involves the application of a dry, free-flowing powder to the surface of an object. This powder is then heat-cured to create a hard, durable, and attractive finish.
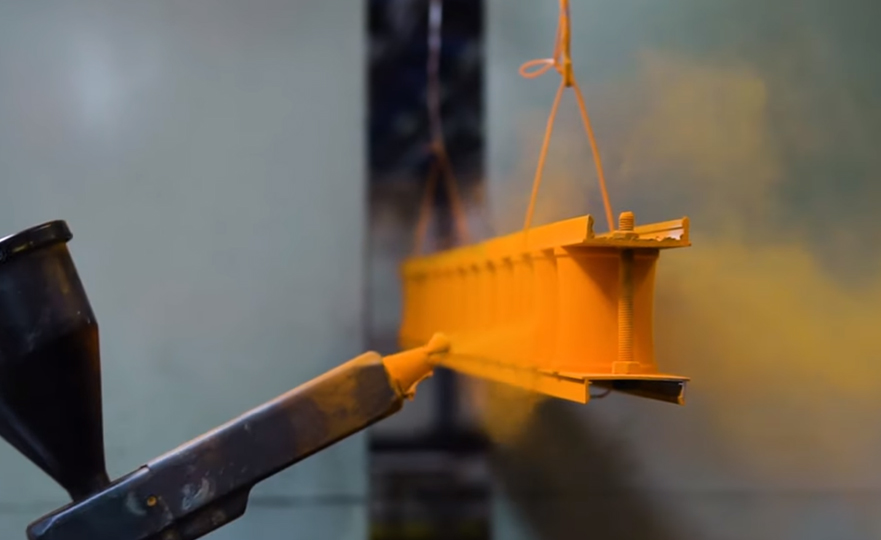
Can Aluminum be Powder Coated?
Yes, aluminum can be powder coated. Powder coating is a versatile finishing method that can be applied to various materials, including aluminum. It offers a durable and attractive finish while providing protection against corrosion and wear. This makes powder coating a popular choice for aluminum products in various industries, including automotive, architectural, and household appliances.
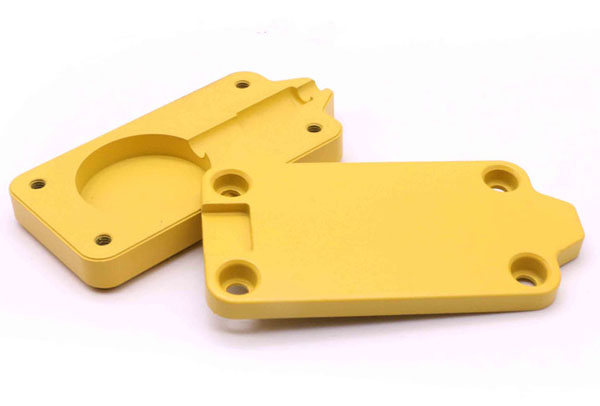

Why Choose Aluminum Powder Coating? Can Plastic be Powder Coated?
Choosing aluminum powder coating offers several advantages:
Durability: Aluminum powder coating provides a robust and long-lasting finish. It is resistant to chipping, cracking, and peeling, ensuring that the aluminum product remains attractive and functional for an extended period.
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum is susceptible to corrosion, especially when exposed to moisture and harsh environments. Powder coating acts as a protective barrier, guarding the aluminum against corrosion and rust.
Aesthetics: Powder coating allows for a wide range of color options and finishes, enhancing the appearance of aluminum products. This versatility makes it an excellent choice for both decorative and functional applications.
Environmental Benefits: Powder coating is an environmentally friendly choice. It produces no volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and generates minimal waste, making it a sustainable finishing option.
As for whether plastics can be powder coated, the answer is yes. While metal surfaces are the most common substrates for powder coating, certain types of plastics can also be powder coated. However, the plastic material needs to be specially formulated to withstand the high-temperature curing process involved in powder coating. Thermosetting plastics are typically used for powder coating applications because they can handle the curing temperatures. It's essential to consult with a professional to determine the suitability of a specific plastic for powder coating and to ensure the proper process is followed.
Which Metals are Suitable for Powder Coating Finishes?
Several metals material are suitable for powder coating surface treatment due to their compatibility with the process and the benefits it offers. Here are some of the metals commonly used for powder coating:

Steel: Steel is one of the most commonly powder-coated metals. It provides excellent adhesion and durability, making it ideal for various applications, from automotive parts to outdoor furniture.
Aluminum: Aluminum is another popular choice for powder coating. It offers corrosion resistance and a lightweight yet durable finish, making it suitable for architectural elements, automotive components, and more.
Cast Iron: Cast iron can be powder coated to provide protection against rust and corrosion. It's often used for items like garden furniture and decorative pieces.
Galvanized Steel: Galvanized steel is coated with a layer of zinc, which enhances its resistance to corrosion. Powder coating can further improve its appearance and durability.
Stainless Steel: While stainless steel is naturally corrosion-resistant, powder coating can be applied for aesthetic purposes or to achieve specific colors or finishes.
Copper and Brass: These metals can also be powder coated to protect them from tarnishing and to create unique decorative finishes.
Magnesium: Powder coating can enhance the corrosion resistance of magnesium, making it suitable for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Bronze: Bronze can be powder coated to maintain its appearance and protect it from environmental factors.
It's important to note that the success of powder coating on a particular metal depends on factors such as surface preparation, the choice of powder coating material, and the curing process. Consulting with a professional or a powder coating specialist is advisable to ensure the best results for your specific metal and application.
Powder Coating Process
The powder coating process involves several essential steps to achieve a durable and high-quality finish on various surfaces. Here is an overview of the typical powder coating process:
Surface Preparation: The first step is to prepare the surface of the object to be coated. This involves cleaning the surface to remove dirt, grease, rust, and any other contaminants. Proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving adhesion and a smooth finish.
Application of Powder: Once the surface is clean and ready, a dry, free-flowing powder is applied to it. The powder consists of finely ground particles of pigment and resin. There are different methods for applying the powder, including electrostatic spraying, fluidized bed dipping, or manual application.
Electrostatic Charging: In electrostatic spraying, the powder particles are given an electrostatic charge. This is done to ensure that the powder adheres uniformly to the grounded object. The electrostatic charge creates a strong attraction between the powder and the surface, minimizing overspray.
Coating Thickness Control: The thickness of the powder coating is controlled by adjusting the powder flow rate and the application time. This step ensures that the desired thickness is achieved for the specific application.
Curing: After the powder is applied, the coated object is moved into an oven or curing chamber. The curing process involves exposing the object to high temperatures (typically between 350°F to 450°F or 175°C to 232°C). During curing, the powder particles melt and fuse together to form a continuous, solid film. This step is crucial for achieving the final finish and durability of the coating.
Cooling: After curing, the coated object is allowed to cool down to room temperature. This step ensures that the powder coating hardens and becomes a durable, smooth finish.
Quality Inspection: The coated object undergoes a thorough inspection to check for any imperfections, such as bubbles, runs, or uneven coverage. Any defects are addressed before the final product is approved.

Packaging and Shipping: Once the quality control checks are complete, the finished product is packaged and prepared for shipping or delivery to the customer.
It's worth noting that the specific details of the powder coating process may vary depending on the type of powder, the equipment used, and the object being coated. Powder coating is a versatile method used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, architectural, and more, to provide durable and attractive finishes on a wide range of products.
Powder Coating Thickness
The thickness of a powder coating can vary depending on several factors, including the type of powder used, the application method, and the specific requirements of the coating project. Typically, powder coatings are applied within a range of 1.5 to 4.5 mils (or 38 to 114 microns) in thickness. Here's a breakdown of these thickness ranges:
Thin Coatings (1.5 to 2.0 mils or 38 to 50 microns): Thin powder coatings are often used for decorative or aesthetic purposes. They provide a smooth finish and are suitable for products like furniture, appliances, and architectural components. These coatings offer good coverage while maintaining fine details on the surface.
Standard Coatings (2.0 to 3.0 mils or 50 to 76 microns): This thickness range is common for most powder coating applications. It provides a balance between durability and appearance. Standard coatings are used in various industries, including automotive, industrial equipment, and outdoor products, to provide protection against corrosion and wear.
Thicker Coatings (3.0 to 4.5 mils or 76 to 114 microns): Thicker powder coatings are chosen when increased durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions are required. They are often used in heavy-duty applications, such as agricultural equipment, construction machinery, and marine components. Thicker coatings offer enhanced protection against abrasion and chemical exposure.
It's essential to note that the desired coating thickness should align with the specific needs of the product and its intended use. Achieving the correct thickness involves careful control of the powder application process, including adjusting the powder flow rate, application time, and curing parameters. Proper quality control measures, such as coating thickness measurement devices, are often used to ensure that the specified thickness range is met consistently.
Ultimately, the choice of powder coating thickness should consider factors such as the substrate material, environmental conditions, and the performance requirements of the coated product. Consulting with a powder coating professional can help determine the optimal thickness for a particular application.
Key Factors in Powder Coating Color Selection
Choosing the right color for a powder coating is an important decision, as it not only affects the aesthetics of the finished product but also plays a role in functionality and branding. Here are some key considerations when selecting a color for powder coating:
Aesthetic Appeal: The color should align with the desired look and style of the product. Consider whether a bold, vibrant color or a more subdued, neutral tone best suits the design.
Brand Identity: If the product represents a brand, the color choice should reflect the brand's identity and values. Consistency in color across products can help with brand recognition.
Environmental Factors: Consider the environment in which the product will be used. For outdoor applications, colors that resist fading due to UV exposure and harsh weather conditions are essential. In contrast, indoor products may have more flexibility in color choice.
Visibility and Safety: In some applications, such as road signs or safety equipment, color choice can impact visibility and safety. High-visibility colors like bright orange or yellow are often chosen for safety reasons.
Temperature Resistance: If the product will be exposed to high temperatures or extreme heat, select a color that can withstand those conditions without discoloration or degradation.
Corrosion Resistance: Some coatings come with additional properties, like corrosion resistance. In such cases, the color choice may affect the overall performance of the coating.
Customization: Powder coatings can be customized to match specific colors or meet unique design requirements. Custom color matching allows for creativity and personalization.
Regulatory Compliance: In certain industries, specific color standards or regulations may apply. Ensure that the chosen color complies with any relevant standards or guidelines.
Application Technique: Different application techniques, such as two-coat systems or metallic finishes, can provide unique visual effects. Explore these options to achieve specific textures or appearances.
Market Preferences: Consider the preferences of the target market or customer base. Understanding what colors are popular or in demand can influence your choice.
Sample Testing: Before proceeding with a large-scale coating project, it's advisable to conduct sample testing to ensure that the selected color meets your expectations and performance requirements.
Remember that powder coatings offer a wide range of colors and finishes, from standard solid colors to metallic, textured, and even special effects coatings. Consulting with a powder coating professional or supplier can help you make an informed decision and provide guidance on the best color options for your specific application.
What Colors can be Powder Coated?
Powder coating is a versatile finishing method that offers a wide range of color options to meet various design and application needs. Here are some of the colors that can be achieved with powder coating:
Solid Colors: Powder coatings are available in a vast array of solid colors, including but not limited to:
Red
Blue
Green
Yellow
Black
White
Gray
Brown
Metallic Colors: Metallic finishes can be achieved by incorporating metallic particles into the powder coating. This creates a shimmering effect, similar to the appearance of metallic paints. Common metallic colors include:
Metallic silver
Metallic gold
Bronze
Copper
Textured Finishes: Powder coatings can create textured finishes that add depth and character to the surface. Textures can include:
Wrinkle
Hammertone
Sandpaper
Antique
Pearlescent and Iridescent Colors: These coatings contain special pigments that create a pearlescent or iridescent effect, where the color appears to change or shift when viewed from different angles.
Custom Colors: Custom color matching allows you to create unique, proprietary colors to suit your specific design or brand requirements. Powder coating suppliers can work with you to achieve the exact shade you desire.
High-Visibility Colors: For safety applications, high-visibility colors like bright orange, yellow, and fluorescent hues are available to enhance visibility and alertness.
Color Combinations: Two-coat powder coating systems can be used to achieve color combinations or layered effects. This involves applying one color as a base coat and another as a topcoat for a unique finish.
Special Effects: Some powder coatings offer special effects, such as sparkle, glimmer, or texture, to create distinctive appearances.
Custom Graphics and Logos: Powder coatings can also be used to apply custom graphics, logos, and designs on surfaces, allowing for branding or decorative elements.
Color Matching: If you have a specific color in mind that is not readily available, many powder coating suppliers can provide color matching services to create a powder coating that precisely matches your desired color.
It's important to work closely with a reputable powder coating supplier or professional to explore the full spectrum of color options and finishes available. They can provide guidance on selecting the most suitable color for your application and ensure that the chosen powder coating meets your performance and aesthetic requirements.
Does Powder Coating Weaken Aluminum?
No, powder coating typically does not weaken the strength of aluminum. In fact, when applied correctly, powder coating can provide additional protection to aluminum surfaces without compromising their inherent strength. Here are a few key points to consider:
Thickness of the Coating: Powder coating is applied as a relatively thin layer, typically ranging from 1.5 to 4.5 mils (38 to 114 microns) in thickness. This thin layer does not significantly alter the dimensions or structural integrity of the aluminum.
Adhesion: Properly applied powder coating adheres well to the aluminum surface, creating a strong bond. This bond enhances the overall durability of the aluminum product by protecting it from corrosion, abrasion, and environmental factors.
Corrosion Protection: Powder coating acts as a barrier against moisture, chemicals, and corrosive substances. This protective layer can actually increase the lifespan of aluminum products by preventing corrosion and oxidation, which can weaken the metal over time.
Impact Resistance: Powder coatings are known for their impact resistance. They can help prevent dents, scratches, and other forms of surface damage that might otherwise compromise the structural integrity of aluminum.
Thermal Properties: Powder coatings can provide thermal insulation to some extent, which can be beneficial in applications where temperature control is important. However, this effect is generally minimal and does not significantly affect the mechanical properties of aluminum.
Proper Application: It's crucial to ensure that the powder coating is applied correctly, following industry standards and guidelines. When done right, the coating enhances the aluminum's properties rather than weakening them.
In summary, powder coating is a protective and decorative finishing method that can enhance the longevity and appearance of aluminum products while maintaining their structural strength. However, like any surface treatment, it should be applied correctly to achieve the desired results. Proper surface preparation, coating thickness control, and curing are essential factors in ensuring the coating's effectiveness without compromising the aluminum's strength.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder Coating
Certainly, here are the advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of powder coating:
Advantages (Pros) of Powder Coating:
Durable Finish: Powder coating provides a durable and long-lasting finish that is resistant to chipping, fading, and wear. It can extend the lifespan of coated products.
Corrosion Resistance: Powder coating offers excellent protection against corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor and harsh environments.
Wide Color Range: There is a vast range of colors and finishes available, allowing for customization and design flexibility.
Environmental Friendliness: Powder coating generates minimal waste and contains no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it an eco-friendly choice.
Efficiency: The powder coating process is efficient, with minimal overspray and material wastage. Overspray can be collected and reused.
Uniform Coating: Powder coating provides a uniform and consistent finish, even on complex or irregularly shaped objects.
High-Quality Appearance: It delivers a high-quality, attractive finish with good color retention and gloss.
Chemical Resistance: Powder coatings can resist exposure to various chemicals, making them suitable for industrial applications.
Cost-Effective: Over time, powder coating can be cost-effective due to its durability, reduced maintenance, and long-term performance.
Quick Curing: Powder coatings cure rapidly during the baking process, saving time in production.
Disadvantages (Cons) of Powder Coating:
Initial Equipment Costs: Setting up a powder coating system can be expensive, including the purchase of specialized equipment like spray guns and curing ovens.
Limited Thickness: Powder coatings are typically applied as thin layers, limiting their ability to cover deep imperfections or provide heavy coatings.
Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is essential for adhesion, and any contaminants or rust must be removed before coating.
Color Change Difficulty: Changing colors with powder coating can be challenging and may require cleaning the equipment thoroughly.
Not Suitable for All Materials: While versatile, powder coating is not suitable for all materials, such as heat-sensitive plastics.
Recovery of Overspray: The collection and reuse of overspray powder require specialized equipment and maintenance.
Skill Requirement: Proper application of powder coating requires skill and training to ensure consistent results.
Limited Repair Options: Touching up or repairing damaged powder coatings can be challenging and may not provide an exact match.
Curing Time: The curing process may take time, affecting production schedules.
In summary, powder coating offers many advantages, including durability, environmental benefits, and a wide range of colors. However, it also has some drawbacks, such as initial equipment costs and limitations in coating thickness. The choice to use powder coating should be based on the specific needs of the project and the desired balance between its pros and cons.
What Surface Effects do Powder-Coated Aluminum Parts Exhibit?
Powder-coated aluminum parts can exhibit a variety of surface effects and finishes, depending on the type of powder coating material and application method used. Here are some common surface effects and finishes you can achieve with powder-coated aluminum:
Smooth and Solid Colors: The most common surface effect is a smooth, solid color finish. Powder coating provides a uniform and consistent appearance, with a wide range of color options. This finish is ideal for achieving a sleek and clean look on aluminum parts.
Textured Finishes: Textured finishes can be applied to powder-coated aluminum parts to create a tactile surface. Examples of textured finishes include:
Wrinkle texture: Provides a textured appearance with a wrinkled pattern.
Hammertone texture: Mimics the look of hammered metal.
Sandpaper texture: Offers a rough, textured surface.
Metallic Finishes: Powder coatings can achieve metallic effects that simulate the appearance of metal surfaces like silver, gold, bronze, and copper. These finishes add a metallic shimmer and depth to the aluminum.
Gloss Levels: Powder coatings can vary in gloss levels, allowing you to choose between high gloss for a shiny appearance or matte finishes for a subdued and non-reflective look. Semi-gloss and satin finishes are also available.
Pearlescent and Iridescent Effects: Special powder coating formulations can create pearlescent and iridescent effects on aluminum surfaces. These effects produce a shifting, multi-color appearance when viewed from different angles.
Texture Combinations: Some powder coatings offer combinations of textures and colors. For example, a textured finish can be combined with a metallic effect to create a unique and eye-catching surface.
Custom Graphics and Logos: Powder coating allows for the application of custom graphics, logos, and designs onto aluminum parts. This customization can enhance branding or add decorative elements to the surface.
Clear Coats: Clear powder coatings can be applied to protect the natural appearance of aluminum while providing a durable and protective layer against corrosion and wear.
Antique or Distressed Finishes: Specialized powder coating techniques can achieve antique or distressed looks on aluminum parts, giving them a weathered and aged appearance.
It's important to note that the specific surface effect and finish depend on the chosen powder coating material, color, and the expertise of the powder coating professional or supplier. When selecting a powder coating finish for your aluminum parts, consider the intended use, design preferences, and the desired visual impact to ensure the best result for your project.
Powder Coating and Other Surface Treatments: Differences, Effects and Cost Comparison
Certainly, let's compare powder coating to some other common surface treatment methods in terms of differences, effects, and cost considerations:
1. Powder Coating vs. Paint:
Differences:
Powder coating involves the application of a dry powder to the surface, while paint uses liquid solvents.
Powder coating is applied electrostatically and then cured, while paint relies on solvent evaporation and drying.
Paint may require a primer coat, whereas powder coating often does not.
Effects:
Powder coating provides a thicker and more durable finish than paint.
Powder coating is resistant to chipping, fading, and corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Paint can offer more color variety and is easier to change or touch up.
Cost Comparison:
Powder coating tends to have higher initial equipment and material costs but can be cost-effective over time due to its durability and reduced maintenance.
Paint may have lower initial costs but can require more frequent repainting and maintenance, which can add up over time.
2. Powder Coating vs. Anodizing (for Aluminum):
Differences:
Powder coating creates a thicker layer on the aluminum surface, while anodizing forms a thin oxide layer through an electrochemical process.
Anodizing alters the aluminum's surface at a molecular level, whereas powder coating is a surface coating.
Anodizing can provide improved corrosion resistance for aluminum.
Effects:
Powder coating offers a broader range of colors and finishes, making it more versatile for design aesthetics.
Anodizing enhances the natural appearance of aluminum while providing corrosion protection.
Powder coating is thicker and more impact-resistant.
Cost Comparison:
Powder coating may have higher initial costs but provides design flexibility and a wide range of color options.
Anodizing is generally less expensive initially but offers fewer color choices and may require a secondary treatment for color variation.
3. Powder Coating vs. Plating (e.g., Chrome Plating):
Differences:
Powder coating is a dry, solvent-free process, while plating involves submerging the object in a chemical bath.
Plating adds a thin metal layer to the surface, while powder coating adds a thicker polymer layer.
Powder coating does not involve hazardous chemicals typically associated with plating processes.
Effects:
Powder coating offers a broader color range and is less prone to chipping and peeling than plated finishes.
Plating can provide a high-gloss, metallic appearance with a mirror-like finish.
Powder coating is more environmentally friendly due to its lack of hazardous chemicals.
Cost Comparison:
Powder coating usually has lower initial costs and is less labor-intensive than plating.
Plating may offer a distinct visual appeal but can be more expensive due to materials and processing complexity.
The choice between powder coating and other surface treatment methods depends on factors such as the specific application, desired appearance, durability requirements, and budget considerations. Each method has its unique advantages and is suited to different situations.
Powder Coating Surface Treatment Applications
Powder coating surface treatments find wide-ranging applications across various industries due to their durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal. Here are some common applications of powder coating surface treatments:
Automotive Parts: Powder coating is used on automotive components such as wheels, bumpers, grilles, engine parts, and frames. It provides corrosion resistance and enhances the appearance of vehicles.

Architectural Elements: Powder coating is applied to architectural features like aluminum doors, window frames, railings, and façades. It offers weather resistance and decorative finishes for buildings.
Furniture: Metal and aluminum furniture, including outdoor seating, tables, and garden furniture, benefit from powder coating for both durability and attractive finishes.
Household Appliances: Appliances like refrigerators, stoves, and washing machines are often powder coated to provide a sleek and durable finish.
Outdoor Equipment: Playground equipment, park benches, and bicycle racks use powder coating to withstand outdoor conditions and provide vibrant colors.
Industrial Equipment: Machinery, equipment, and tools used in various industries are powder coated for corrosion resistance, impact resistance, and a professional appearance.
Agricultural Equipment: Farm machinery, including tractors, plows, and harvesters, is often powder coated to withstand rugged outdoor environments.
Electronics Enclosures: Powder coating is used for the protective coating of electronic enclosures and cabinets to shield sensitive equipment from environmental factors.

Lighting Fixtures: Outdoor and indoor lighting fixtures benefit from powder coating to maintain their appearance and protect against weather-related damage.
Medical Equipment: Many medical devices and equipment are powder coated for a durable, easy-to-clean, and hygienic surface.
Aviation and Aerospace Components: Aircraft parts and components, as well as aerospace equipment, use powder coating to meet strict industry standards and ensure resistance to harsh conditions.
Marine Applications: Boat and marine equipment, including hulls, railings, and accessories, utilize powder coating for corrosion resistance in saltwater environments.
Retail Displays and Signage: Retail displays, shelving units, and signage benefit from powder coating to maintain a clean and attractive appearance.
Custom Fabrications: Custom metal fabrications, such as art installations, sculptures, and architectural features, often employ powder coating for both protection and aesthetic enhancement.

Bicycles and Sporting Goods: Bicycles, sports equipment, and fitness gear use powder coating for durable and customizable finishes.

Fire Hydrants and Safety Equipment: Fire hydrants, safety barriers, and emergency equipment are powder coated for visibility, durability, and resistance to harsh conditions.
Electrical Enclosures: Electrical cabinets and enclosures are powder coated to protect sensitive electrical components and maintain their integrity.
Powder coating offers these applications a balance between protection, appearance, and customization. Its ability to resist corrosion, impact, UV radiation, and chemicals, combined with a wide range of available colors and finishes, makes it a popular choice for a diverse range of products and industries.
Problems and Precautions for Powder Coated Aluminum Parts
When dealing with powder coating aluminum parts, there are several common issues and important considerations to keep in mind to ensure a successful coating process and a high-quality finish. Here are some key problem areas and precautions:
Common Issues:
Surface Preparation: Inadequate surface preparation is a common problem. Ensure that the aluminum surface is thoroughly cleaned, degreased, and free of any contaminants, oxidation, or corrosion. Inadequate surface prep can lead to poor adhesion and coating failure.
Aluminum Alloy Selection: Different aluminum alloys have varying levels of suitability for powder coating. Ensure that you are using the appropriate alloy for your application. Some alloys may require special pretreatment processes.
Proper Grounding: The electrostatic nature of powder coating requires proper grounding of the aluminum part and the powder coating equipment. Inadequate grounding can result in uneven powder application.
Powder Application Technique: Proper technique during powder application is essential. Ensure an even and consistent application to avoid issues like uneven thickness or orange peel texture.
Curing Temperature and Time: Incorrect curing temperatures or durations can result in incomplete curing, leading to coating defects or poor adhesion. Follow manufacturer recommendations for curing parameters.
Powder Contamination: Keep the powder and application equipment clean to prevent contamination, which can result in defects in the finish.
Masking and Hanging: Proper masking of areas not intended for coating and hanging of parts during the curing process is critical. Improper masking can lead to overspray and uneven coating.
Important Considerations:
Aluminum Pretreatment: Depending on the aluminum's condition, pretreatment processes like chemical etching or conversion coating may be necessary to enhance adhesion and corrosion resistance.
Thickness Control: Monitor the thickness of the powder coating to ensure it falls within the desired range. Too much or too little coating can affect the finish and performance.
Humidity and Temperature: Environmental factors like humidity and temperature can impact the curing process. Ensure that conditions are suitable for proper curing.
Quality Control: Implement quality control measures to inspect finished parts for defects, such as bubbles, runs, or uneven coverage. Address any issues before finalizing the product.
Storage and Handling: Store powder coatings properly in a dry, cool environment to prevent moisture absorption or contamination. Handle parts with care to avoid damage to the coating.
Color Matching: If color consistency is crucial, work with a reputable powder coating supplier to ensure accurate color matching, especially for large or batched orders.
Equipment Maintenance: Regularly maintain and clean powder coating equipment to ensure consistent and reliable performance.
Consult Professionals: If unsure about any aspect of the powder coating process or if dealing with complex or critical applications, consult with experienced professionals or powder coating specialists.
By addressing these common issues and adhering to important considerations, you can achieve a successful and high-quality powder coating finish on your aluminum parts. Proper preparation, attention to detail, and adherence to best practices are key to a successful powder coating project.
Conclusion
Do you know how to choose the right finish for your project? VMT has 15 years of experience in surface treatment experts to choose the appropriate surface treatment for you to improve the surface texture and performance of CNC parts.
Learn about the powder coating surface treatment process, benefits and applications in this article. If you want to know more about powder coating surface treatment, please contact us today. VMT can provide a wide range of CNC machining and manufacturing capabilities and surface treatment services for steel, aluminum, titanium, copper and other materials. Our team of professional engineers can choose the appropriate surface treatment for you to meet all your CNC machined parts production needs and obtain the best results. Best, competitive price. Why not give VMT a try and contact us now to get a quote.
Powder Coating FAQs
Certainly! Here are some common questions and answers regarding powder coating:
1. What is powder coating?
Powder coating is a dry finishing process where a free-flowing, electrostatically charged powder is applied to a surface and then cured with heat to form a durable, protective, and decorative coating.
2. How does powder coating work?
Powder coating works through a process of electrostatic attraction. The powder is sprayed onto a grounded object, and the charged particles adhere to the surface. The coated object is then cured in an oven, causing the powder to melt and fuse into a smooth, durable finish.
3. What are the advantages of powder coating?
Advantages of powder coating include durability, resistance to chipping and fading, corrosion resistance, a wide range of color options, environmental friendliness (low VOC emissions), and the ability to coat complex shapes and surfaces.
4. What materials can be powder coated?
Metals such as steel, aluminum, copper, and stainless steel are commonly powder coated. Some heat-resistant plastics can also be powder coated.
5. Can I apply powder coating at home?
While it's possible to apply powder coating at home with the right equipment and setup, it is typically done by professionals or in specialized facilities due to the need for proper curing ovens, electrostatic guns, and expertise in the process.
6. How do I choose the right powder coating color?
The choice of color depends on your application, aesthetics, and branding. Consider factors like environment, visibility, and personal preferences. Many suppliers offer color samples and can assist in color selection.
7. Is powder coating environmentally friendly?
Yes, powder coating is considered environmentally friendly because it generates minimal waste, contains no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and has low emissions during the curing process.
8. Can powder coating be repaired or touched up?
Powder coating can be challenging to repair or touch up, especially if the damage is extensive. Small touch-ups may be possible with specialized powder coating pens or patches, but it's generally recommended to recoat the entire surface for a seamless finish.
9. How thick is a typical powder coating layer?
Powder coatings are typically applied within a range of 1.5 to 4.5 mils (38 to 114 microns) in thickness, depending on the application and performance requirements.
10. What industries use powder coating?
Powder coating is used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, architecture, furniture, appliances, aerospace, agriculture, marine, electronics, and more.
11. Can powder coating be used for outdoor applications?
Yes, powder coating is suitable for outdoor applications. It provides excellent protection against UV radiation, moisture, and harsh weather conditions, making it ideal for items like outdoor furniture and architectural elements.
12. How do I maintain powder-coated surfaces?
To maintain powder-coated surfaces, clean them regularly with mild soap and water. Avoid abrasive cleaners or tools that may damage the finish. Promptly address any scratches or damage to prevent corrosion.
These are some of the common questions and answers about powder coating. If you have specific questions or need guidance on a particular aspect of powder coating, it's advisable to consult with a powder coating professional or supplier for expert advice.
