15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory

Hey there I’m VMT Sam!
With 25 years of CNC machining experience we are committed to helping clients overcome 10000 complex part-processing challenges all to contribute to a better life through intelligent manufacturing. Contact us now
 165 |
Published by VMT at Apr 20 2022
165 |
Published by VMT at Apr 20 2022
CNC machining stands for computer numerical control machining and is often used in different CNC machining manufacturing sectors. CNC machining technology provides a multi-faceted automated process that can produce high-quality CNC machined parts in large quantities. Features such as extreme precision, efficiency and mechanization make it the perfect choice for several CNC machining manufacturers.
CNC Machining Manufacturing Process
The creation of a finished product using humans, machines, tools, and biological or chemical processing is called the manufacturing process. Manufacturing can either mean converting raw materials into finished goods on a large scale, or producing more complex CNC-machined products by producing basic products for other manufacturers to produce CNC-machined parts for medical, electronics, automotive, and more.
Raw materials are transformed into final products using various CNC machining manufacturing processes. Manufacturing starts with product design and suitable material selection. The material is then transformed using various CNC machining manufacturing processes to create the finished product.
There are various types of manufacturing processes. But we will discuss three common manufacturing processes that are widely used.
Subtractive CNC Machining Process
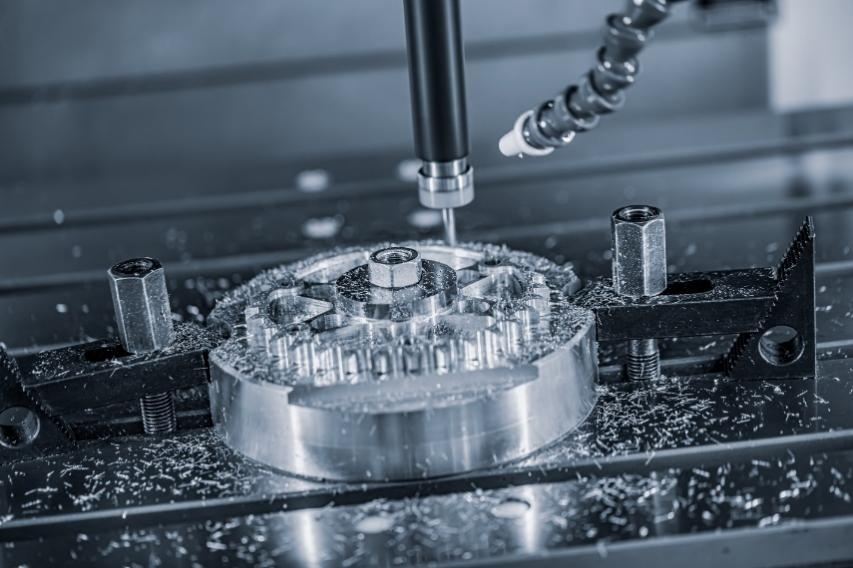

A process for manufacturing CNC machined parts by continuously cutting material into the desired final shape and size through a controlled material removal process. The subtractive process can be performed by manually cutting the material, but is most commonly done using CNC machining machines.
Additive Manufacturing Process
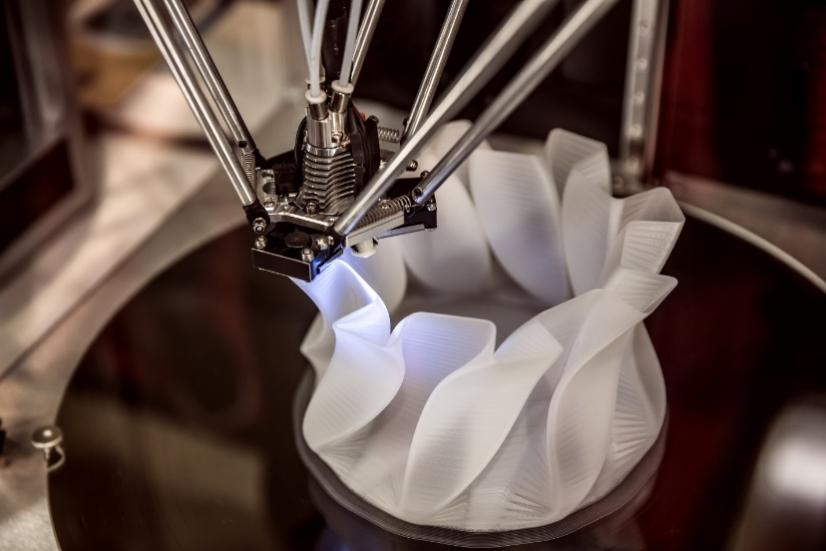
Additive manufacturing is sometimes referred to as 3D printing. An advanced technique that creates 3D objects using successive layers of material deposited from digital 3D design data. Unlike subtractive manufacturing processes that remove material, additive manufacturing builds CNC machined parts layer by layer from material provided in fine powder form.
Forming Manufacturing Process
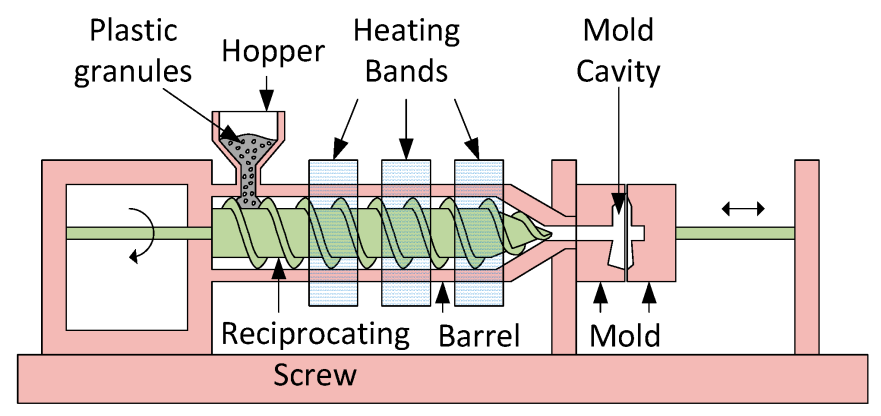
This manufacturing process utilizes stresses such as compression, tension, shear, etc., or some combination of these stresses, to plastically deform the material into the desired shape and size. such as injection molding. This manufacturing process is commonly used for plastic and metal materials. No material is added or subtracted during this process.
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process in which a piece of material is converted into a custom CNC machined part with the help of coded program instructions and different machine tools.
This subtractive cutting technology provides the most complex designs that can be mass-manufactured at faster speeds and with high precision. The process is controlled by computer-coded program instructions that reduce the margin for error that can be critical in some cases.
CNC machining equipment can repeatedly execute similar coded program instructions as needed to support the manufacture of previously CNC machined parts. There are different versions of CNC machines depending on the level of complexity. Some machines can grab a workpiece or tool and move it along three axes (X, Y, and Z). But some precision machines can move the workpiece or tool along three axes, and can also rotate along the a, b (or c) axes.

CNC Machining Workflow
CNC machining was originally just numerical control (NC) using punched tape cards, during the introduction of computers to what is now known as computer numerical control (CNC). It utilizes computer-controlled instructions to manipulate and machine stock materials into custom CNC parts by manipulating machines and different cutting tools.
The basic CNC machining workflow can be divided into four main steps.
First, we craft highly intelligent designs using software called CAD. Second, we create instructions based on designs that describe how to carve. This process is called CAM. Then the machine is setting up, and finally, we hand these instructions to the machine, which is usually done through a digital interface. After completing these steps, we click the start button and the machine will cut out the design.
Let's discover every step thoroughly
Design CAD
CAD stands for Computer Aided Design and it is software for creating CAD designs of 2D vector or 3D solid parts. Using this software, we can create models of parts or products with the most accurate technical specifications. Once the design is created, the designer then exports the file to a CNC-supported file format such as STEP or IGES.
Generate CAM Code
At this stage, CAD design files are converted into programming code using CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software. Then, it decides on CNC machines and different tools to produce the parts.
The programming languages used in the CNC machining process include G code and M code. The language that controls and instructs machine tool movements to achieve the desired shape is called G-code (G-code stands for general or geometric code). The M code stands for Miscellaneous Code, which controls miscellaneous machine actions, including starting and stopping any specific action or program during machining.
Once the CAM code is generated, it is then transferred to the machine.
Machine Settings
Before operating a CNC machine, set up the machine for proper operation. The workpiece is held in the correct position and attached with the required tools such as drills and other tools for accurate and efficient product results.
Execute Machining Action
Computer-integrated CAM-generated G-code and M-code programming instructions instruct machines and tools when and how to perform specific machining actions. When the computer goes through all the programming codes and the machine executes them accordingly, we get the final custom product. In this way, you can obtain complex parts or products for mass production.
CNC machining is used to manufacture components in virtually every industry and application. Precision technology can handle almost any material one can think of. It provides a wide range of materials to obtain the basic properties of the final product.
Metal
It can process many metals such as aluminum, brass, titanium, steel, etc. Most preferred, however, are metals that provide the desired product quality.
Plastic
CNC machined plastics include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), nylon, acrylic, polycarbonate, and more.
Wood
The use of wood is relatively infrequent. Hardwood, plywood, cork, etc. are among the commonly used materials.
Foam
Foams have many applications in different industries. Sculpted foam and rigid foam are mainly used for CNC machining.
Which Industries Use CNC Machining?
CNC machining is used in one way or another in almost every industry worldwide. Especially large manufacturers prefer it. It is becoming a valuable asset for manufacturing complex parts for different industries. Several important industries that rely on precision machining are:
Advantages of CNC Machining
CNC machining is favored by many industries because of its unparalleled advantages. It provides streamlined, convenient and precise manufacturing capabilities for creating mass production. Computer numerically controlled processes also offer many financial and production advantages over other traditional and advanced manufacturing techniques. Below is a compilation of the main advantages of CNC machining:
Increased Productivity
CNC machining sites can run longer, and workshops can meet production demands by operating 24/7 with little or no human intervention. Since CNC machining machines are automated through programming. It empowers CNC machining equipment to automate a complex series of different processes. Meanwhile, energy can be spent on other things. This ultimately brings productivity.
CNC Machining Cost-Effective
CNC machining is not only about its initial cost of manufacture, but also with a high emphasis on yield and accurate products. Computer-controlled instructions reduce the risk of manufacturing errors. Training employees to operate CNC machines is not that much of a hassle. Effortless design customization and fewer opportunities for error avoid cost planning delays and material scrap. CNC machining technology requires less manpower, which also reduces the price. All of these factors contribute to a cost-effective CNC machining operation. Therefore, it offers prototyping and batch CNC machining at very reasonable prices.
High-Precision CNC Machining Parts Production
CNC machining processes are automated and computerized, which considerably reduces human involvement and opportunities for error. It offers tight tolerances (for metal and plastic parts that can withstand extreme pressures and temperatures), outstanding mechanical efficiency and exceptional machining accuracy. This makes CNC machining a high-precision machining technique.
Faster Turnaround
The precision CNC machining process completes the production process faster than other manufacturing techniques. It starts with designing a CAD file. During the design phase, almost all possibilities and obstacles are removed. Material selection, tools, finishing methods, etc. are summarized at the beginning. Then it only takes time to create the CAM code and the machine will be ready to engrave the product. It takes much less time than other processes.
Safety
CNC machining machines are very safe to use because they are designed to operate with maximum safety. Most of the time, these machines operate behind guards or even closed, transparent safety doors. Workers are immune to any splashing sharp tools, hot material, paper jams or other machining errors. Any uncertain safety issue will only cause harm to the machine, not the operator.
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!