15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 0 |
Published by VMT at Dec 11 2025 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
0 |
Published by VMT at Dec 11 2025 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
You might be struggling to understand why tungsten stands out among metals. Its extreme density makes it unique, but that same property can complicate material handling and machining. The good news is, by understanding the density of tungsten and its characteristics, you can make smarter choices for CNC machined parts, reduce costs, and ensure your projects run smoothly.
The density of tungsten is approximately 19.254 g/cm³, making it one of the heaviest metals used in industry. Its high tungsten metal density allows for compact, durable components ideal for CNC machined parts. By understanding its weight per unit volume and specific gravity, you can optimize design, reduce material waste, and improve performance in demanding applications.
Now that you know tungsten’s impressive specific density and weight density, it’s time to explore how to calculate and measure its density accurately. Understanding these methods will help you select the right CNC machining services and optimize your CNC machined parts for precision, performance, and cost-efficiency.
Tungsten is known for its remarkable heaviness. Its tungsten material density is about 19.254 g/cm³, which is nearly twice that of lead and more than five times that of aluminum. This high tungsten metal density makes it ideal for applications requiring compact, heavy, and durable components, from aerospace parts to radiation shielding.

To calculate the tungsten mass density, you divide the metal’s mass by its volume. The formula is simple:
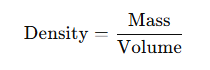
For example, if you have a tungsten piece weighing 1925 grams with a volume of 100 cm³, its tungsten specific gravity is 19.254 g/cm³. This calculation is essential for designing CNC machined parts with precise weight and balance.
Tungsten’s extreme density comes from its atomic structure. Each tungsten atom is heavy, and the atoms are packed tightly in a body-centered cubic crystal lattice, leaving little empty space. This combination of high atomic mass and compact arrangement results in its extraordinary tungsten weight density and specific weight, making it much heavier than most metals.
Measuring tungsten specific density accurately is essential for applications where precision matters. Different methods allow you to determine tungsten weight density and tungsten mass density depending on your sample size and required accuracy. Proper measurement ensures your CNC machined parts meet performance standards and reduces the risk of costly errors.
Ohmic Pulse Heating Method
This method uses a controlled electric pulse to heat a tungsten sample rapidly. The temperature rise is then measured and used to calculate tungsten metal density. It is highly precise and ideal for small, high-purity tungsten samples.
Precision Weighing and Volume Measurement
The most common method involves weighing the tungsten sample and measuring its volume using geometric calculations or displacement techniques. Using the formula Density = Mass ÷ Volume, you can determine the tungsten material density accurately.
Archimedes' Hanging Drop Method
This technique measures the density of tungsten by suspending a sample in a liquid and recording the apparent weight change. This allows calculation of tungsten specific gravity without cutting the material. It’s especially useful for irregularly shaped samples.
Machining of Tungsten Surfaces
Tungsten’s high density makes CNC machining challenging. Accurate density measurement before machining ensures correct tool selection and reduces wear. Understanding the tungsten weight per unit volume helps you predict cutting forces and plan for efficient material removal.
This section explains why tungsten’s high density is valuable in industrial and scientific applications. Its exceptional tungsten metal density enables compact, heavy-duty components that improve performance, durability, and efficiency in various fields. Understanding these benefits helps you design better CNC machined parts and select suitable CNC machining services.
Key Points:
Tip: When designing CNC machined parts with tungsten, factor in its density early to reduce material waste and tooling issues.
This section highlights how tungsten’s high density compares with other metals and alloys. Understanding these comparisons helps you evaluate material selection for CNC machined parts, optimize weight and performance, and make informed decisions in design and manufacturing.

Density Comparison Table (g/cm³)
| Material |
Density (g/cm³) |
| Density of Tungsten |
19.254 |
| Density of Osmium |
22.59 |
| Density of Tungsten Oxide |
7.16 |
| Density of Platinum |
21.45 |
| Density of Tungsten Carbide |
15.63 |
| Density of Steel |
7.85 |
| Density of Gold |
19.32 |
| Density of Lead |
11.34 |
| Density of Aluminum |
2.70 |
| Density of Titanium |
4.51 |
| Density of Stainless Steel |
7.75 – 8.0 |
| Density of Copper |
8.96 |
| Density of Iron |
7.87 |
| Density of Tin |
7.31 |
| Density of Silver |
10.49 |
| Density of Zinc |
7.14 |
Summary of Tungsten Density Comparison
Tip: Always factor in tungsten’s weight per unit volume when comparing materials to avoid design or machining issues.
Tungsten’s high density makes it a critical material in industries where weight, durability, and compactness matter. Its exceptional tungsten metal density allows designers to create CNC machined parts that are both strong and space-efficient.
Key Applications:
Tip: When planning CNC machined parts with tungsten, consider its tungsten specific weight to optimize tooling, reduce material waste, and maintain safety.
Tungsten stands out as one of the densest metals, with a tungsten metal density of approximately 19.254 g/cm³. Its extraordinary weight per unit volume and specific gravity make it ideal for compact, durable, and high-performance CNC machined parts. Understanding how to calculate, measure, and compare its density with other metals helps you make informed material choices, optimize design, and reduce costs. High-density tungsten finds applications across aerospace, defense, medical, and industrial machinery, proving that mastering its properties is key to achieving precision, efficiency, and reliability in any project.
1. Why does tungsten have a high density? Is tungsten the densest metal?
Tungsten’s high density comes from its heavy atoms and tightly packed body-centered cubic crystal structure. While extremely dense (19.254 g/cm³), it is not the absolute densest metal—osmium (22.59 g/cm³) is denser.
2. Is tungsten the densest metal?
No, tungsten is one of the densest metals used in industry, but osmium and platinum are slightly denser. Tungsten is valued for its combination of density, hardness, and machinability.
3. Is tungsten a very heavy metal?
Yes, tungsten is extremely heavy compared to most common metals like aluminum, steel, or titanium. Its high tungsten weight per unit volume makes it ideal for compact, heavy-duty components.
4. Does tungsten rust or corrode easily?
Tungsten is highly resistant to corrosion and does not rust easily under normal conditions. However, at very high temperatures or in certain chemical environments, it may oxidize slowly.
5. Does pure tungsten rust?
No, pure tungsten does not rust like iron or steel. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for long-lasting CNC machined parts.
6. What are the three densest metals?
The three densest naturally occurring metals are:
7. Why is tungsten used in heavy-duty applications?
Tungsten’s high mass density, strength, and durability make it ideal for aerospace, defense, medical shielding, and industrial machinery. Its ability to provide heavy-duty performance in compact components is unmatched by most metals.
